Nuclear Polarization Surface Enhanced NMR Spectroscopy
Discerning γ-Alumina Surface Sites with Nitrogen-15 Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Surface Enhanced NMR Spectroscopy of Adsorbed Pyridine
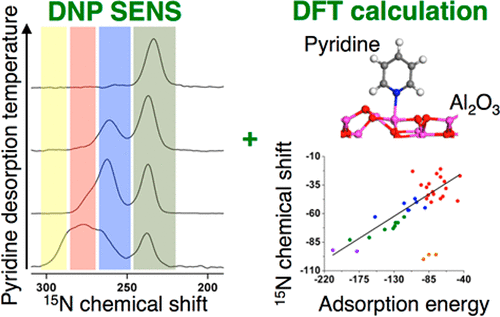
In this study, low-temperature nitrogen-15 dynamic nuclear polarization surface enhanced NMR spectroscopy (DNP SENS) of adsorbed pyridine in combination with FTIR measurements and DFT calculations was applied to investigate the surface sites of γ-alumina, which can be divided into four groups: (1) groups 1 and 2, associated with less shielded 15N chemical shifts and the lowest ν(8a) frequencies of adsorbed pyridine, corresponding to weakly adsorbed H-bonded pyridine to hydroxyl group or chemisorbed water on alumina; (2) group 3, with intermediate 15N chemical shifts and ν(8a) frequencies, corresponding to pyridine coordinated to specific Lewis acid sites, namely five-coordinated (AlV) aluminum atoms of the (100) facet, as well as some H-bonded pyridine; (3) group 4, associated with the most shielded 15N chemical shift and the highest ν(8a) frequency, selectively assigned to Lewis acid Al sites located on the (110) facet and corresponding to both four- and five-coordinated aluminum atoms (AlIV and AlV). Noteworthy, a correlation between the 15N chemical shift and the adsorption energy of pyridine, that is H-bonded or coordinated to Al Lewis acid sites, was identified: the stronger the adsorption, the more shielded the 15N chemical shift. According to Natural Chemical Shielding (NCS) analysis, this behavior is traced back to the bonding interaction of the lone pair of pyridine and the Lewis acid or OH sites which controls a specific principal component of the chemical shift tensor of pyridine on one hand, and the adsorption energy on the other hand. This correlation between 15N chemical shift and adsorption energy is likely general since it has a well-defined molecular origin and can thus be extended to other oxides.
Access the paper published in the external pageJournal of Physical Chemistry Ccall_made.